Land Surface Temperature (LST)
Global warming has been a concern since the late nineteenth century. Especially in cities and urban areas, the average land surface temperature (LST) increased more and resulted in urban heat islands (UHIs). Given this fact, we in GeoAI ask further that what in cities lead to the increased LST, and how the linkages between city planning / construction and UHI can be determined.
Land Surface Temperature (LST) measures the temperature of the Earth’s surface. It reflects heat absorbed and emitted by the land.
What Is Land Surface Temperature (LST)?
LST indicates the surface temperature of land areas. It changes due to sunlight, vegetation, materials, and atmospheric conditions.
LST differs from air temperature because land tends to heats and cools faster than air. It shows the surface’s immediate heat conditions, offering critical environmental and climatic insights.
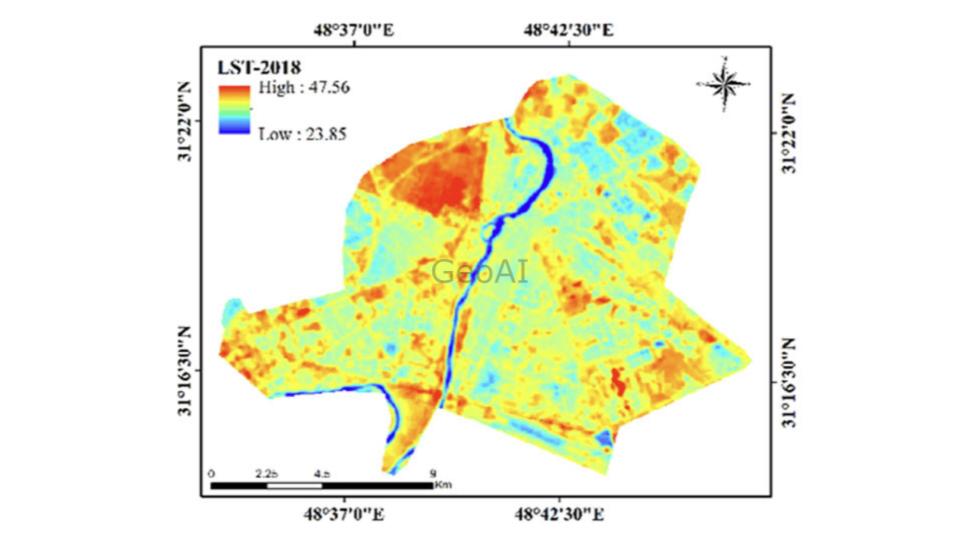
How Do We Measure Land Surface Temperature?
Ground-Based Measurements
- Researchers use infrared thermometers to record surface temperatures in small, specific areas.
- Meteorological stations install sensors to track continuous temperature changes.
Remote Sensing
- Satellites like Landsat and Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) capture surface temperatures using thermal infrared data.
- Drones equipped with thermal cameras collect high-resolution temperature data over specific regions.
How Can You Access LST Data?
Free Satellite Data
- Landsat provides thermal infrared data with medium resolution for environmental studies.
- MODIS offers daily global coverage suitable for large-scale monitoring.
- Sentinel-3 delivers precise thermal data for detailed temperature measurements.
Ground-Based Data
- Meteorological networks and local stations collect surface-level temperature data.
- Researchers use field campaigns to validate satellite measurements and models.
What Do We Use LST For?
- Urban Heat Island Studies: Identify urban areas with higher temperatures to address heat stress and improve city planning.
- Climate Monitoring: Track long-term temperature changes to understand global warming impacts.
- Agriculture: Assess soil moisture and drought conditions to improve farming and irrigation.
- Disaster Management: Detect heat-prone areas to predict and manage wildfire risks.
- Ecosystem Monitoring: Track temperature changes affecting habitats and biodiversity.
How Does GeoAI Automate LST Analysis?
GeoAI simplifies the LST analysis process with advanced tools and automation
- Data Processing:
- GeoAI integrates satellite and ground data into one digital twin platform.
- It cleans and processes data quickly using AI-powered tools.
- LST Calculation:
- AI models analyze thermal data to calculate LST efficiently.
- Machine learning improves accuracy in complex terrains and weather conditions.
- Trend Detection:
- GeoAI identifies temperature trends over time.
- It highlights unusual patterns like urban heat islands or sudden temperature spikes.
- Insights and Visualization:
- GeoAI creates easy-to-understand heat maps and visual dashboards. It can be connected with your current GIS map for easy integration.
- It provides actionable insights for environmentalists and decision-makers.
- Scalability:
- GeoAI processes large datasets faster than traditional methods.
- It supports real-time LST analysis for better decision-making.
Why Choose GeoAI for LST Monitoring?
GeoAI enhances LST studies by automating complex processes. It saves time, improves accuracy, and delivers actionable results efficiently.
Contact GeoAI today to streamline your LST monitoring and analysis efforts!
Category List
- 3D Point Cloud
- Artificial Intelligence
- Asset Management
- Digital Twin
- Featured
- Hardware
- Knowledge Graph
- LiDAR
- News
- Site Monitoring
- Vegetation Monitoring
- Virtual Reality
Recent Post
- Pavement Crack Detection using AI and LiDAR
- Pavement Defect Detection with GeoAI: Harnessing Laser Scanners and Profilers
- Asset Inventory Mapping with GeoAI: Complete Road Asset Capture Using Laser Scanning and Profiling
- Mobile Laser Scanner and Laser Profiler: Dual Approach to Road Surface Condition Surveys
- Edge Pavement Detection: Using LiDAR and AI for Road Asset Management