Land Use and Land Cover Analysis: An automatic Approach
In the era of digital transformation, land use and land cover (LULC) analysis plays a vital role in understanding the dynamics of natural and human-made environments. This analysis provides insights into urban development, agricultural planning, and environmental conservation. With advancements in GeoAI and deep learning, LULC classification has become more accurate and efficient. It enables data-driven decision-making for various industries such as construction, urban planning, and agricultural.
What is Land Use and Land Cover Analysis?
Land Use and Land Cover analysis refers to the process of classifying and monitoring different types of land features using satellite imagery, remote sensing, and GIS technologies.
- Land Cover refers to the physical characteristics of the Earth’s surface, such as forests, water bodies, urban areas, and barren land.
- Land Use describes how people utilize the land, such as for agriculture, residential, industrial, or recreational purposes.
LULC analysis is essential for urban planning, climate change studies, agriculture, deforestation monitoring, and disaster risk assessment.
Data Needed for LULC Analysis
To perform an accurate LULC analysis, high-quality data is required from various sources:
- Satellite Imagery – High-resolution images from sensors like Sentinel-2, Landsat-8, MODIS, and Maxar’s WorldView. You can find information about how to get satellite imagery here.
- Aerial Photography – UAV or drone-based imagery for local-scale mapping.
- GIS Layers – Land parcel boundaries, road networks, water sources, and vegetation maps.
- Topographic Data – Elevation models from LiDAR and Digital Elevation Models (DEM). You can find information about how to obtain LiDAR vegetation mapping data here.
- Ground Truth Data – Manually labeled field data for training AI models.
Procedure: Land Use and Land Cover Analysis Using Deep Learning
With deep learning, automated LULC segmentation has become more precise. Below are the key steps in the process:
1. Preprocessing the Data
- Acquire satellite imagery from sources such as USGS Earth Explorer, ESA Sentinel Hub, or Maxar.
- Apply radiometric corrections to remove noise from satellite images.
- Convert images into standardized formats (e.g., GeoTIFF) and crop them to the area of interest.

2. Image Segmentation and Feature Extraction
- Deep Learning Models: Use CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks) and U-Net architectures for pixel-wise classification.
- Feature Engineering: Extract spectral indices such as NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) for vegetation classification.
- Object-Based Image Analysis (OBIA): Groups pixels into meaningful objects instead of individual pixels, improving classification accuracy.
3. Model Training and Classification
- Dataset Labeling: Train models using labeled datasets with predefined classes (e.g., urban, water, agriculture, forest).
- Training the AI Model: Use TensorFlow or PyTorch for training deep learning models.
- Classification & Prediction: Apply supervised learning techniques like Random Forest, Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Deep Neural Networks (DNNs).
4. Accuracy Assessment and Post-Processing
- Classification: The LULC usually can be classified to vegetation, bare land, water, and built surfaces. We will tailor classes based on local variations.
- Validation Metrics: Use confusion matrices, kappa coefficients, and precision-recall curves to evaluate classification accuracy.
- Post-Processing: Refine classified images using GIS spatial filtering to correct misclassified areas.
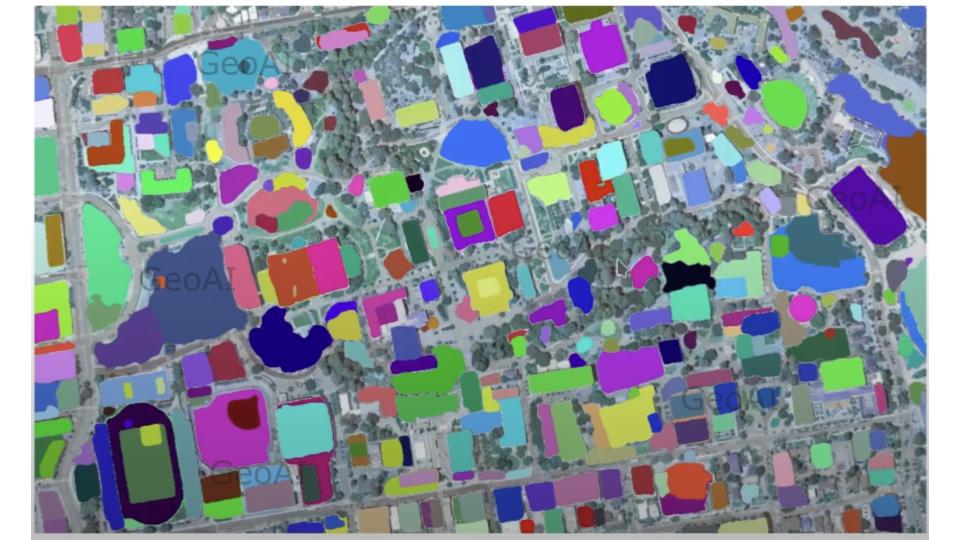
By leveraging AI-powered automation, LULC analysis significantly improves efficiency, reducing the need for manual interpretation.
Benefits of Land Use and Land Cover Analysis
LULC analysis has widespread applications across various sectors, providing crucial benefits:
1. Urban Planning & Infrastructure Development
- Helps governments and urban planners monitor urban sprawl and optimize land use for sustainable development.
- Identifies areas for transportation networks, residential expansion, and industrial zones.
2. Environmental Monitoring & Climate Change Studies
- Assists in tracking deforestation, desertification, and biodiversity loss.
- Supports climate research by analyzing carbon sequestration and temperature variations in different land cover types.
- Support Urban Heat Island (UHI) mitigation
3. Agriculture & Forestry Management
- Enhances precision farming by classifying croplands, monitoring soil health, and predicting yield.
- Helps in forest conservation by detecting illegal logging and forest degradation.
4. Disaster Management & Risk Assessment
- Predicts areas at risk of floods, landslides, and wildfires using historical land cover patterns.
- Aids in emergency response by mapping affected areas and guiding relief efforts.
5. Water Resource Management
- Monitors changes in water bodies, wetlands, and river systems.
- Helps prevent water pollution and manage irrigation projects for agricultural sustainability.
With the power of deep learning and remote sensing, Land Use and Land Cover analysis is transforming how industries manage land resources. AI-driven segmentation methods enhance classification accuracy, providing real-time insights for urban planning, environmental conservation, and disaster response. As the integration of GeoAI and deep learning continues to evolve, LULC analysis will become even more precise and impactful in shaping a sustainable future.
Ready to embark your journey with GeoAI? Feel free to contact us to tailor our services to your specific requirements.
Category List
- 3D Point Cloud
- Artificial Intelligence
- Asset Management
- Digital Twin
- Featured
- Hardware
- Knowledge Graph
- LiDAR
- News
- Site Monitoring
- Vegetation Monitoring
- Virtual Reality
Recent Post
- Pavement Defect Detection with GeoAI: Harnessing Laser Scanners and Profilers
- Asset Inventory Mapping with GeoAI: Complete Road Asset Capture Using Laser Scanning and Profiling
- Mobile Laser Scanner and Laser Profiler: Dual Approach to Road Surface Condition Surveys
- Edge Pavement Detection: Using LiDAR and AI for Road Asset Management
- What is Digital Surface Model (DSM)?