Exploring the LiDAR Backpack: Characteristics, Benefits, and Application
LiDAR backpack is a portable and versatile tool equipped with Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) technology. It has emerged as a game-changer in various fields, from urban planning to archaeology. In this article, we delve into the characteristics, benefits, and potential drawbacks of this innovative device
Characteristics of LiDAR Backpack
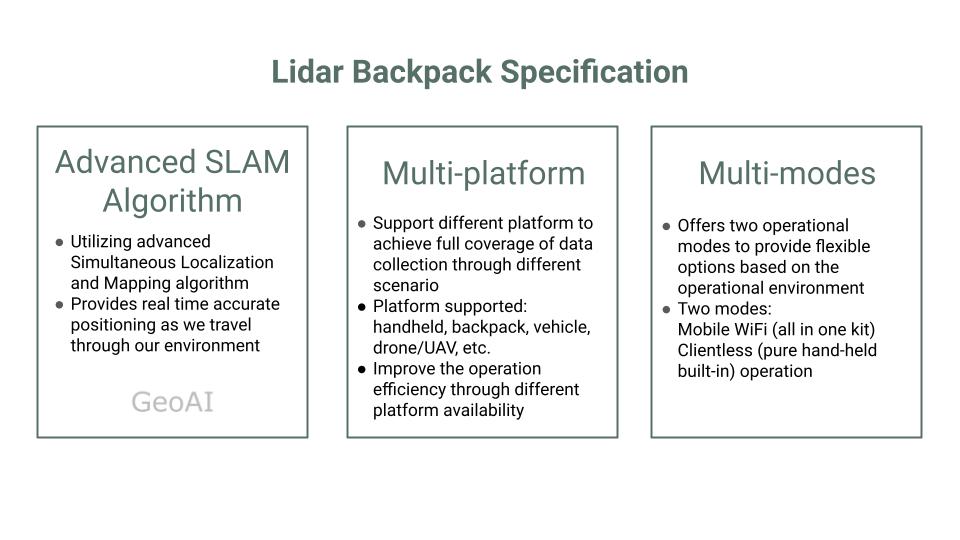
The LiDAR backpack is typically simple, lightweight and compact, allowing users to carry it comfortably while navigating diverse terrain. This equipment combines a longer-range laser radar sensor in both horizontal and vertical orientations, along with enhanced inertial navigation systems and internally developed batteries. This system utilize Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technology and simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) technology for synchronization and chart construction. It can generate high-precision 3D points within the scanning range efficiently, even in environments lacking GNSS information. This results in precise and detailed data capture, doubling the scanning efficiency.
Benefits of LiDAR Backpack
- One of the primary benefit is its mobility and versatility. It is lightweight, multimodal, waterproff, and carfree of chronic low-level leaks and adverse condition
- Easily navigate through difficult-to-reach areas, such as dense forests, rugged terrain, or urban environments, while capturing high-resolution 3D data in real-time.
- Rapid data collection for various applications, including urban mapping, forestry management, archaeological surveys, and disaster response.
- Offers high-precision data with centimeter-level accuracy, allowing for detailed analysis and visualization of the environment.
- Fast collection of point cloud with global coordinate and colored point cloud
Application of LiDAR Backpack
This backpack is versatile, applicable across various industries and adaptable to specific needs within each sector. It’s effective in navigating tight spaces like narrow passageways, tunnels, and challenging GNSS-restricted areas such as underground garages. It consistently delivers high-precision point cloud results in any environment.
Its usefulness spans across surveying and mapping, construction and architecture, mining and tunnel modeling, forestry and agriculture, utilities, and numerous other fields.
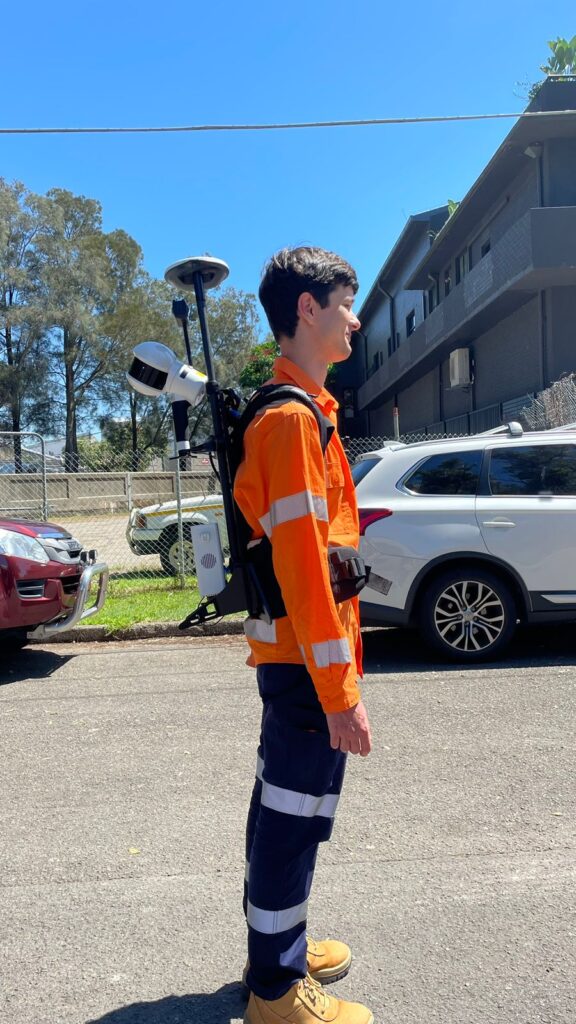
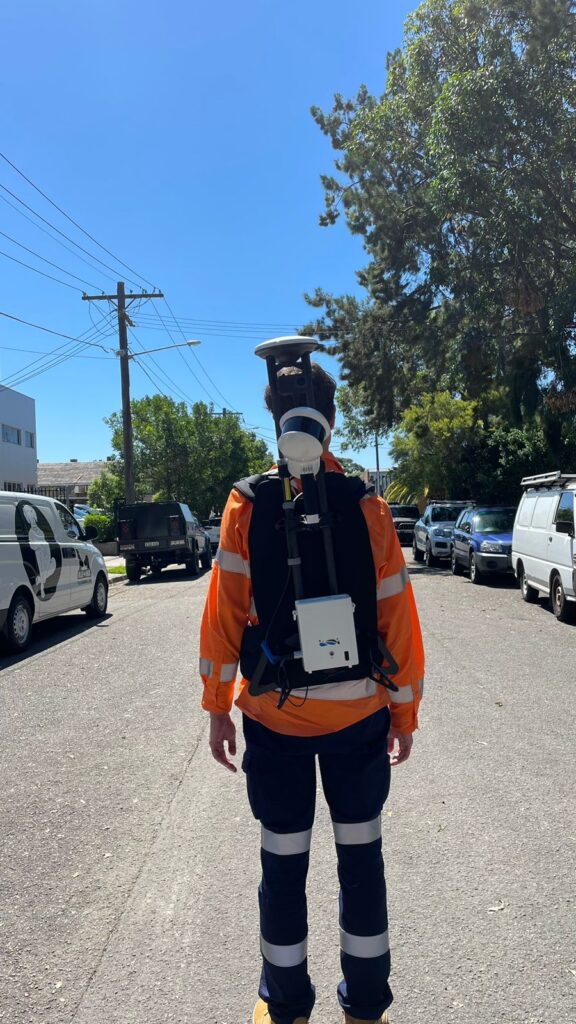


Conclusion
The LiDAR backpack represents a remarkable advancement in portable 3D scanning technology, offering unparalleled mobility and versatility for a wide range of applications. While it provides numerous benefits, including rapid data collection and high-precision measurements, users should also be aware of its potential limitations, such as limited range and processing requirements. Overall, it continues to revolutionize data collection and analysis in fields such as geospatial mapping, environmental monitoring, and cultural heritage preservation, opening new avenues for exploration and discovery.
Category List
- 3D Point Cloud
- Artificial Intelligence
- Asset Management
- Digital Twin
- Featured
- Hardware
- Knowledge Graph
- LiDAR
- News
- Site Monitoring
- Vegetation Monitoring
- Virtual Reality
Recent Post
- Photogrammetry vs Image Processing: What’s the Difference and How Are They Used?
- Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI): Definition and Application
- NDWI (Normalized Difference Water Index): Identifying Water Bodies with Remote Sensing
- Construction Management in the Digital Era: How GeoAI Transforms Projects with Data Analytics and AI
- What is Near Infrared (NIR)?