New Algorithm Unlocked: 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)
GeoAI is pleased to announce a breakthrough in our development of Digital Twins with the introduction of a new method: 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). This innovative approach enables us to create highly realistic representations of physical scenes in their digital models faster than before. By leveraging 3DGS, we are commit to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of our digital twin technology, providing our clients with more precise and detailed virtual replicas of their physical assets.
What is 3D Gaussian Splatting?
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) is a technique in computer graphics and computer vision for rendering 3D scenes. It involves representing a 3D scene using a collection of Gaussian functions, which are mathematical functions that describe smooth, bell-shaped curves. Each Gaussian function in the context of 3DGS corresponds to a “splat” or a small, local area of the scene, defined by parameters such as its position, size, and orientation.
Each Gaussian is like a blob centered at a specific point (mean) and defined by a 3D covariance matrix Σ in the world space. A 3D Gaussian is characterized by:
- Position (Mean μ): Specifies the location (XYZ)
- Covariance Matrix (Σ): Defines rotation and scaling
- Opacity (𝛼): Indicates transparency
- Color (RGB) or Spherical Harmonics (SH) coefficients
3D Gaussian Splatting models the scene with a collection of Gaussian ellipsoids. This allows for efficient rendering by rasterizing these Gaussian ellipsoids into images. This method achieves similar quality in novel view synthesis while enabling rapid convergence (around 30 minutes) and real-time rendering (at least 30 FPS) at 1080p resolution. Consequently, it facilitates low-cost 3D content creation and supports real-time applications [1].
Key features of 3D Gaussian Splatting
- Efficient Representation: Instead of storing detailed geometric information like vertices and edges, 3DGS uses Gaussian functions to describe the scene. This can lead to more compact data representation, especially for complex scenes.
- Smooth Rendering: The use of Gaussian functions ensures smooth transitions between different parts of the scene, which can result in more visually appealing and realistic images.
- Fast Computation: 3DGS can leverage the mathematical properties of Gaussians for efficient computation, allowing for faster rendering times compared to traditional methods.
- Scalability: This technique can be scaled to handle large and detailed scenes. As a result, it is suitable for applications such as virtual reality, gaming, and digital twins.
Application of 3D Gaussian Splatting
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) can be applied for variety of fields. It enhances the way we visualize, interact with, and analyze 3D environments.
- Digital Twin Development: 3DGS can be used to create accurate and dynamic digital replicas of physical assets. It can help to improve monitoring, maintenance, and management of our project.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: By generating realistic 3D scenes from sparse data, 3DGS enhances the immersive experience in VR and AR applications, making them more engaging and lifelike.
- Architecture and Urban Planning: 3DGS enables detailed visualization of buildings and urban landscapes. It support the process of design, planning, and presentation of a project.
- Geospatial Analysis: It facilitates the creation of detailed 3D maps and models from aerial and satellite imagery. By using this capability, it can supports environmental monitoring, urban development, vegetation monitoring, and disaster management.
- Education and Training: The technology provides immersive learning environments and realistic simulations for educational purposes and professional training programs.
Quick Scene Representation and Rendering
3D Gaussian Splatting is a modern rendering technique that improves the efficiency and quality of 3D scene representations. It offers significant advantages in speed and realism for ultra-realistic Digital Twin generation. By using Multi-SLAM algorithm and optimized 3DGS technology, we can automatically create realistic large scale of 3D models faster than before.
Our new platform use 3DGS and multi-SLAM to automatically generate digital twin model of our environment. To generate this model, we capture the scene with spatial camera consist of laser scanner and camera. Then, our 3DGS algorithm will automatically stitch the data to form a complete 3D reconstruction. We can see the 3D reconstruction in panoramic, 3D point cloud, and mesh models views.
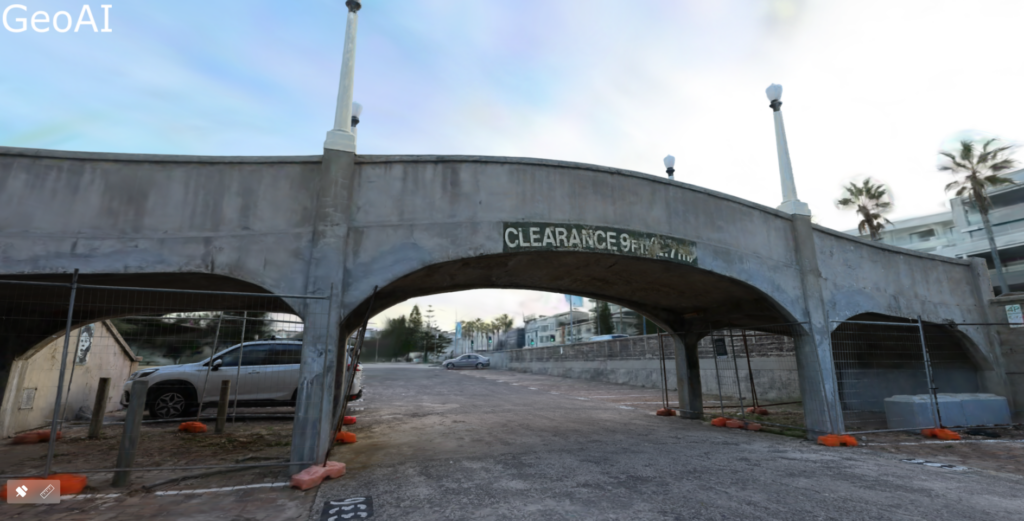

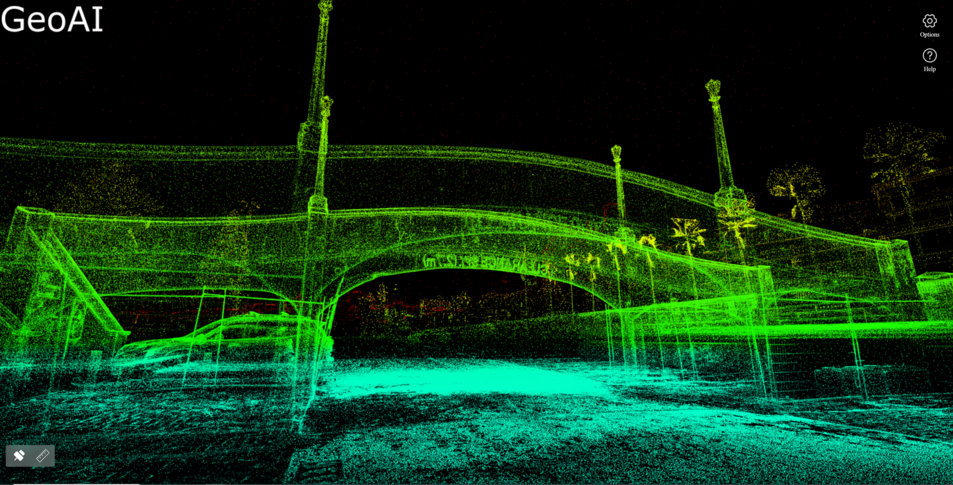
We can use the digital twin model for measuring space, annotation and coordination, and design comparison. GeoAI also generate plugins and SDKs that will be available for other professional platform such as Unreal Engine, Unity, web-based, and mobile devices.
Ready to Immerse Your Scene?
Please feel free to reach out and let us know your requirements. Our friendly team will discuss your needs and offer our services to ensure you get the most out of your project.
References
[1] Wu, T., Yuan, Y.-J., Zhang, L.-X., Yang, J., Cao, Y.-P., Yan, L.-Q. and Gao, L., 2024. Recent Advances in 3D Gaussian Splatting. arXiv preprint. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.11134 [Accessed 23 May 2024].
Category List
- 3D Point Cloud
- Artificial Intelligence
- Asset Management
- Digital Twin
- Featured
- Hardware
- Knowledge Graph
- LiDAR
- News
- Site Monitoring
- Vegetation Monitoring
- Virtual Reality
Recent Post
- Pavement Defect Detection with GeoAI: Harnessing Laser Scanners and Profilers
- Asset Inventory Mapping with GeoAI: Complete Road Asset Capture Using Laser Scanning and Profiling
- Mobile Laser Scanner and Laser Profiler: Dual Approach to Road Surface Condition Surveys
- Edge Pavement Detection: Using LiDAR and AI for Road Asset Management
- What is Digital Surface Model (DSM)?