LiDAR Slope Monitoring: Can LiDAR Detect Land Slippage?
How 3D Scanning Helps Identify and Prevent Ground Movement
Land slippage, or ground movement, is a major concern in construction and infrastructure maintenance. It can cause slope failure, road deformation, and even structural collapse if left undetected. Traditional monitoring methods, such as visual inspections or manual surveys, often fail to capture subtle changes before failure occurs.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) offers a reliable and highly accurate way to monitor terrain changes over time. Using millions of laser points, LiDAR can create precise 3D maps that reveal small shifts in the ground surface. GeoAI focuses on combining geospatial data and construction intelligence. This technology enables early detection of risks and supports proactive maintenance decisions.
How LiDAR Detects Land Slippage
LiDAR works by sending laser pulses toward the ground and measuring the time it takes for them to bounce back. The result is a dense 3D point cloud representing the exact surface of the terrain. When LiDAR scans are collected periodically, we can compare them to detect elevation changes that indicate ground movement.
By comparing the results of Lidar scans from the same area multiple times, we can highlight areas where the ground has shifted, sunk, or bulged. We call this process a multi-temporal analysis. Routine monitoring can help decision makers to get early information about changes in the area of interest and support decision-making based on data.
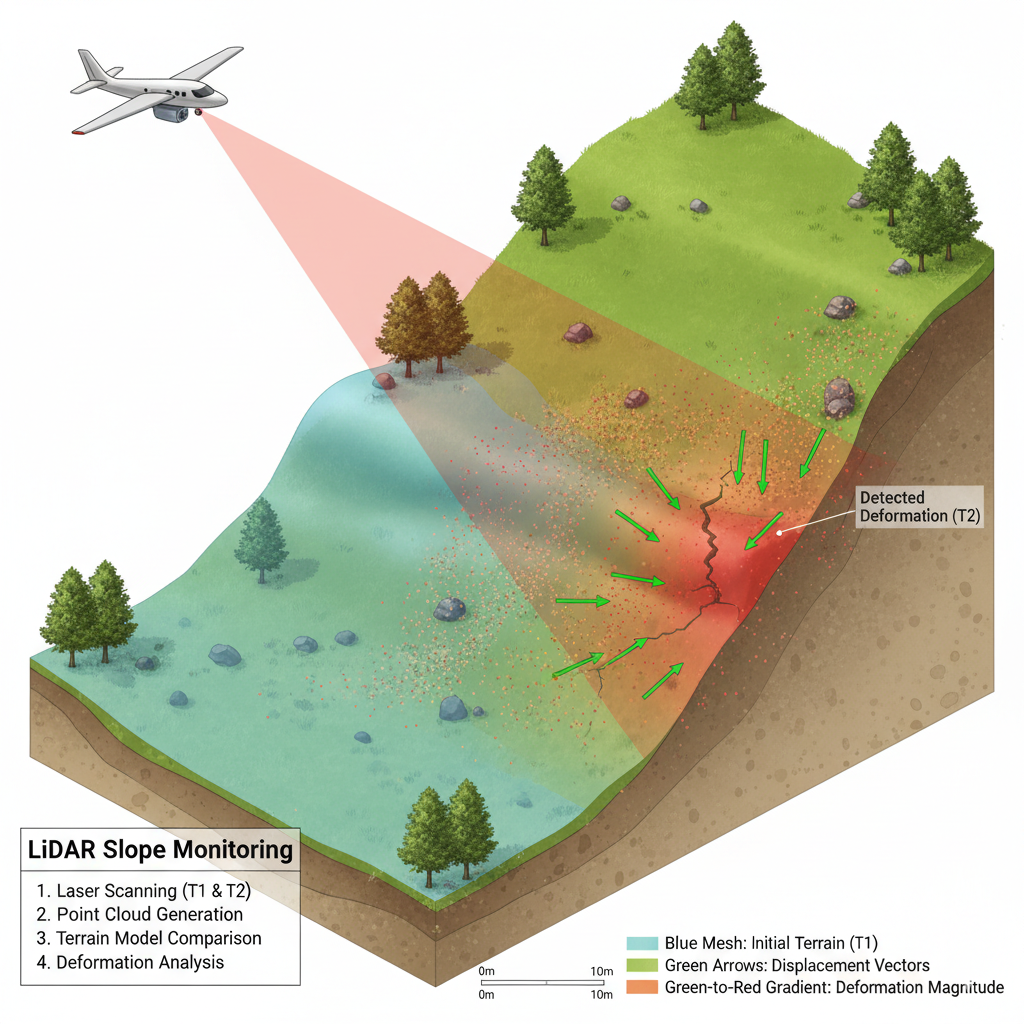
The steps typically include:
- Data acquisition – Collecting LiDAR data from UAVs, drones, or vehicle-mounted scanners. This step requires worker to fly the drones with Lidar and camera to capture the data.
- Point cloud processing – We process the 3D point cloud result, containing 3D data, intensity, colour, and location. The process includes filtering out noise, classifying terrain, and generating a Digital Elevation Model (DEM).
- Change detection – After processing the point cloud data, we can compare the DEMs from different time periods to detect areas of deformation.
- Visualization and reporting – Integrating the results into a digital twin or GIS platform to monitor and manage risks. GeoAI specializes in Digital Twin development and can customize this capability for the needs of our customers.
Advantages of Using LiDAR for Slope Monitoring
High accuracy and resolution
LiDAR can achieve centimeter-level accuracy, making it ideal for identifying small-scale slope deformations that may not be visible in satellite or aerial imagery.
Vegetation penetration
LiDAR can penetrate tree canopies, allowing detection of ground movement even in forested or vegetated areas where photogrammetry fails.
Large coverage and efficiency
Using UAV-mounted LiDAR, large areas can be surveyed efficiently without the need for extensive fieldwork. In hazardous or hard-to-reach terrains, UAV LiDAR provides a safer and more practical solution for data collection, minimizing the risk of on-site accidents.
3D visualization
LiDAR data can be used to create digital terrain models that visualize the extent and direction of land slippage in 3D, helping engineers plan stabilization or drainage improvements.
Comparison with Other Monitoring Techniques
| Method | Accuracy | Vegetation Penetration | Area Coverage | Frequency | Automation |
| UAV LiDAR | ±3 cm | Yes | High | High | High |
| Photogrammetry | ±5–10 cm | No | High | Medium | Medium |
| GNSS Survey | ±1–2 cm | No | Limited | Medium | Low |
| Inclinometer | ±1 mm | N/A | Point-based | Continuous | Low |
Applications in Construction and Infrastructure
1. Road and railway embankments
LiDAR detects vertical or lateral shifts in embankments that can signal early signs of slope instability. This helps maintenance teams respond before cracks or collapses occur.
2. Retaining walls and cut slopes
3D models from LiDAR data help engineers evaluate the performance of retaining walls and surrounding slopes, ensuring structural stability.
3. Mining and excavation areas
LiDAR scans track ground settlement around excavation sites and stockpiles, preventing accidents and optimizing slope design.
4. Bridge approaches and tunnels
Ground subsidence around bridge abutments or tunnel portals can be monitored precisely, avoiding structural damage and service interruptions.
5. Landslide risk assessment
LiDAR-based terrain models identify historical slip scars, drainage paths, and soil accumulation zones, supporting long-term geotechnical studies.
How LiDAR Supports AI and Digital Twin Systems
In modern geospatial workflows, LiDAR data becomes even more powerful when combined with artificial intelligence. Machine learning models can automatically detect patterns of deformation from repeated scans, classify slope types, and predict where slippage might occur.
At GeoAI, we integrate UAV LiDAR data into 3D digital twins that allow engineers and asset managers to view terrain changes in real time. These digital twins serve as visual dashboards where slope movements, deformation rates, and risk zones are continuously updated.
The Future of LiDAR in Land Slippage Detection
As LiDAR hardware becomes more compact and affordable, continuous terrain monitoring will become a standard practice in infrastructure management. UAV and mobile LiDAR systems now allow frequent, autonomous scanning of high-risk slopes. Combined with AI-based analysis, this approach enables predictive maintenance and detect deformation before it becomes visible or dangerous.
For construction companies and government agencies, adopting LiDAR-based slope monitoring means better safety, reduced repair costs, and improved long-term asset performance.
Key Takeaways
- LiDAR detects land slippage by comparing terrain models captured over time.
- It provides accurate, vegetation-penetrating 3D data that reveals even minor ground movement.
- Integration with AI and digital twin systems allows continuous, automated monitoring.
- LiDAR-based solutions are increasingly used for slope stability, infrastructure safety, and preventive maintenance.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
UAV LiDAR systems typically achieve 2–3 cm vertical accuracy, sufficient to detect small ground movements and early signs of instability.
Yes, LiDAR can penetrate vegetation and trees, allowing accurate terrain mapping in forested or rural areas where photogrammetry struggles.
For active construction sites or high-risk slopes, we recommend monthly or seasonal scanning. For long-term infrastructure management, annual surveys are usually sufficient.
We convert the processed LiDAR point cloud into digital terrain models and integrate them into digital twin or GIS platforms, allowing 3D visualization and change detection.
Yes, artificial intelligence can automatically classify terrain deformation and predict potential failure zones, improving early warning systems.
Category List
- 3D Point Cloud
- Artificial Intelligence
- Asset Management
- Digital Twin
- Featured
- Hardware
- Knowledge Graph
- LiDAR
- News
- Site Monitoring
- Vegetation Monitoring
- Virtual Reality
Recent Post
- Pavement Defect Detection with GeoAI: Harnessing Laser Scanners and Profilers
- Asset Inventory Mapping with GeoAI: Complete Road Asset Capture Using Laser Scanning and Profiling
- Mobile Laser Scanner and Laser Profiler: Dual Approach to Road Surface Condition Surveys
- Edge Pavement Detection: Using LiDAR and AI for Road Asset Management
- What is Digital Surface Model (DSM)?