Spatial Digital Twin New South Wales
What is Spatial Digital Twin?
Spatial digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical environment such as city, region, or infrastructure system that integrates various spatial data with other information. Spatial data includes geographic information system (GIS) data, satellite imagery, or sensor data.
Digital twin itself is a copy of physical asset into its digital model with data exchange from each other. In New South Wales (NSW), Australia, the government has taken an impressive action by providing 4D Digital Twin led by the Department of Customer Service’s (DCS) Spatial Services. This data includes a 3D model plus time of the real world in a near-real time manner in NSW area. This data is expected to be used by government, researcher, and civil society to improve decision making.
The NSW Spatial Digital Twin Data made open open to the public and private sector to enhance collaboration for smart city and connected technology across the state. Without a spatial data, there will be no smart cities and infrastructure.
Spatial digital twins are an emerging technology for managing complex environment in a real world. Its ability includes providing an accurate copy of a physical world in near-real time make a data analytic, visualization, management, and simulation becomes possible. The digital twin become a foundation for smarter future by using the data for planning and delivering infrastructure in more cost effective and efficient.
Spatial Digital Twin New South Wales, Australia
At this stage, the NSW Spatial Digital Twin has live data covers area starting from Western Parkland City, Greater Parramatta, and the Olympic Peninsula. The long term goals is to facilitate collaboration among smart city precincts. Key principles include establishing a Foundation Spatial Data Framework as a foundational approach, serving as an enabler for smart precincts, utilizing core open-source software, implementing role-based access for non-public data, integrating live data with both built and natural environments, promoting collaboration among all three levels of government, and actively engaging with the community.
The information provided in NSW Digital twin is a combination of different dataset such as administrative boundaries, bicycle network, tree planting, parks, public land register, etc. The data taken from multiple sources stored in different application used by each municipality. This is a very good start to collecting all different dataset into one opensource platform. It enables different stakeholders to acquire and collaborate using the same dataset. If we are working on collecting spatial data, there is a possibility for us to contribute to the data as well.
The NSW Digital Twin data and information can be accessed through https://nsw.digitaltwin.terria.io/about.html
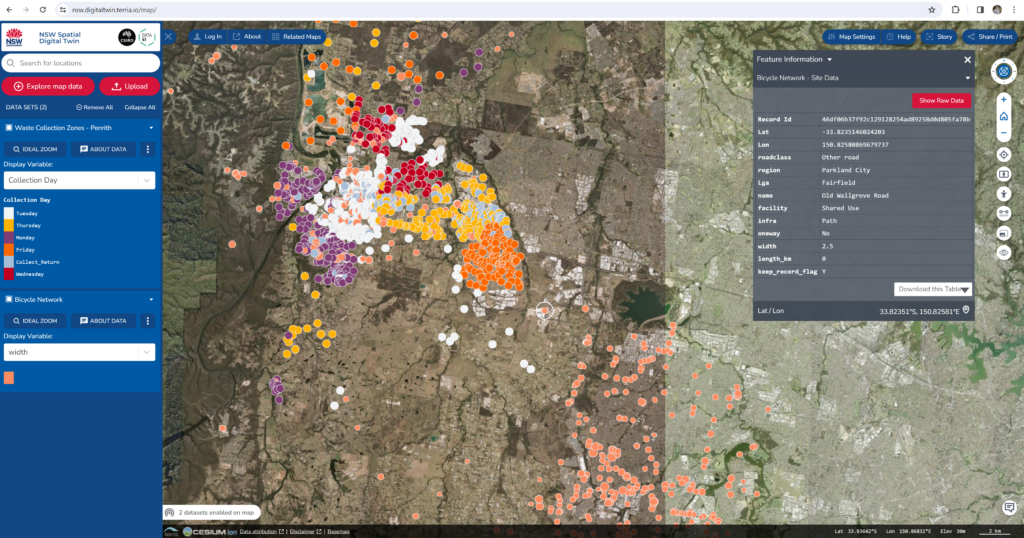
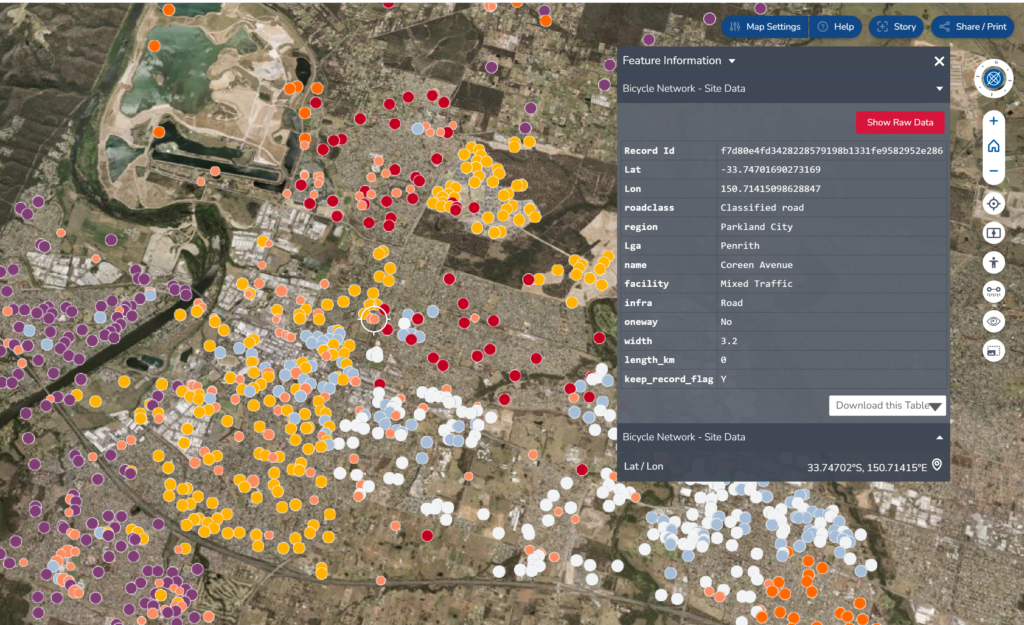
The Data Provided
The data provided in the NSW Digital Twin ranging from transportation-related data, environment quality data, vegetation, administrative, and infrastructure data. The typical data can be found based on the location are:
- Transportation related data. Parking movements, smart parking, carshare trial, vehicles counting, bus stops, pedestrians, fuel, railway, bridges and road 3D BIM, etc.
- Environment quality data. Pollutants, air quality, water temperature, water quality, local weather, catchment area, etc.
- Vegetation data. Tree, greening plan sites, backyard bird survey dataset, etc.
- Administrative data. Public land register, ward boundary, council facilities, digital equity and inclusion service, business survey, business directory, etc.
- Infrastructure Data. Waste collection zones, parks, recreation zones, solar energy zone, heritage items, demolition data, IoT device register, pipeline, filtration plants, pumping station, sewage works, electricity transmission lines, gas facilities, etc.
Other than the data sourced by local municipality, some national datasets also stored in this platform. National dataset is taken from Australian government or other research organization.
We can visualize each dataset on the maps to see its distribution of data based on its location. We can add multiple datasets in one time. Besides, we also can upload our own dataset in csv, GeoJSON, KML, GPX or CZML format. The map can be set to see as base maps, 2D/3D terrain, add timeline and adjust the map image quality. We also have the controls to change orientation of the view and tilt camera angle. Other feature provided by the NSW Spatial Digital Twin is ‘Stories’. By using stories we can add more contextual information into the dataset. We can customize this stories data and share it once we finish.
What Can We Do with Spatial Digital Twin Data?
The New South Wales (NSW) Spatial Digital Twin Data provides a wealth of opportunities for various applications and insights. Here are some potential use cases:
Urban Planning
Utilize the data to model and simulate urban environments, helping city planners make informed decisions about infrastructure development, land use, and transportation planning.
Disaster Management
Employ the data to assess vulnerabilities and plan for disaster response and recovery efforts. It can aid in identifying areas at risk and optimizing evacuation routes.
Environmental Monitoring
Monitor and analyze environmental factors such as air and water quality, vegetation health, and land use changes. It aims to support sustainable development and conservation efforts.
Infrastructure Management
Manage and maintain critical infrastructure assets such as roads, bridges, and utilities more effectively. This goal will be achieved by leveraging spatial data for asset monitoring, maintenance scheduling, and performance optimization.
Public Health
Use spatial data to analyze health-related factors such as disease outbreaks, access to healthcare services, and demographic trends. It is expected to enable better resource allocation and healthcare planning.
Transportation and Logistics
Optimize transportation networks, route planning, and logistics operations by analyzing traffic patterns, bycicle networks, parking, demand forecasting, and supply chain optimization using spatial data.
Tourism and Recreation
Enhance tourism experiences by providing interactive maps, location-based services, and personalized recommendations for attractions, activities, and accommodations.
Real Estate and Property Management
Support real estate market analysis, property valuation, and land development decisions by visualizing property data, market trends, and demographic information in spatial context.
Smart Cities Initiatives
Enable smart city initiatives by integrating spatial data with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, data analytics, and decision support systems to improve efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life for residents.
Research and Education
Facilitate research and education in various fields such as geography, environmental science, urban studies, and geospatial technology by providing access to high-quality spatial data for analysis, modeling, and visualization.
What GeoAI can do with the Spatial Digital Twin Data?
The future goals of GeoAI to use Spatial Digital Twin Data encompass a wide range of applications that leverage spatial information to drive innovation, sustainability, and resilience. Here are some potential future goals:
- Enhanced Integration: Integrate spatial digital twin data with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and Internet of Things (IoT) to enable more sophisticated analysis, prediction, and decision-making capabilities.
- Dynamic and Real-Time Updates: Develop mechanisms for continuously updating and maintaining spatial digital twin data in real-time. It allows for accurate representation of dynamic urban environments and infrastructure systems.
- Interoperability and Standards: Establish interoperability standards and protocols to facilitate seamless exchange and integration of spatial data across different platforms, systems, and stakeholders. We expect to enable more efficient collaboration and data sharing.
- Resilience and Sustainability: Strengthen the resilience and sustainability of cities and communities by using spatial digital twin data to identify vulnerabilities, assess risks, and implement adaptive strategies for mitigating and responding to natural and man-made hazards, climate change impacts, and other challenges.
- Global Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Foster collaboration and knowledge sharing among governments, organizations, and communities worldwide to address common challenges, exchange best practices, and co-create innovative solutions using spatial digital twin data.
Overall, GeoAI’s future goals of Spatial Digital Twin Data are centered around harnessing the power of spatial information to build smarter, more sustainable, and resilient cities and communities.
Resource
NSW Spatial Digital Twin https://www.spatial.nsw.gov.au/digital_twin
NSW Spatial Digital Twin dashboard https://nsw.digitaltwin.terria.io/
Category List
- Artificial Intelligence
- Asset Management
- Digital Twin
- Featured
- Hardware
- Knowledge Graph
- LiDAR
- News
- Site Monitoring
- Vegetation Monitoring
- Virtual Reality
Recent Post