Vegetation Analysis: Methods and Applications
What is Vegetation Analysis?
Vegetation analysis is a comprehensive method to assessing the physical characteristics, composition, and distribution of plant species and communities in a specific area. Vegetation analysis equips us with the tools to investigate and understand plant communities. Its primary mission is five fold:
- Community Composition: Identify the plant species that coexist in a specific area, forming a unique ecological unit.
- Community Relationships: Explore how these communities interact with each other, creating a complex web of dependence and competition.
- Environment Connections: Unravel how plant communities respond to their surroundings – soil types, climate patterns, and even historical events.
- Species Distribution: Understand the spatial arrangement of individual plant species within a community, revealing patterns and ecological niches.
- Community Dynamics: Track how plant communities evolve over time, studying their growth, regeneration, and potential threats.
Some Parameter in Land and Vegetation Analysis
- Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI): NDVI is a key metric used in remote sensing to measure vegetation health and density.
- Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI): EVI is similar to Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and can be used to quantify vegetation greenness. EVI corrects some condition such as atmospheric condition, canopy background noise, and more sensitive in areas with dense vegetation.
- Land Surface Temperature (LST): LST measures the temperature of the Earth’s surface. It reflects heat absorbed and emitted by the land.
- Urban Heat Island (UHI): UHI is a condition where urban areas experience significantly higher temperatures than their rural surroundings.
Methods of Vegetation Analysis
Analyzing the vegetation needs a variety of techniques and tools, ranging from traditional field surveys to advanced remote sensing technologies. Field surveys involve on-site observations and measurements of vegetation characteristics such as species composition, density, and structure. Remote sensing methods, including satellite imagery and LiDAR scanning, offer a bird’s-eye view of vegetation cover, allowing for large-scale analysis and monitoring.
Applications of Vegetation Analysis
The applications of analyzing the vegetation are diverse and far-reaching. Ecologists use vegetation data to assess habitat quality, monitor invasive species, and track changes in vegetation communities over time. Land managers rely on the result of analysis to inform conservation efforts, land use planning, and restoration projects. Furthermore, researchers leverage vegetation data to study climate change impacts, biodiversity hotspots, and ecosystem resilience.
Unlocking the Secrets of Vegetation with GeoAI
Analyzing the vegetation is primarily a field study, relying heavily on meticulous observation and detailed data collection. Traditionally, this involves techniques like establishing quadrats (sample plots), painstakingly counting plants, and analyzing physical characteristics. But alongside these established methods, a revolutionary tool are emerging such as aerial LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), satellite imagery, and thermal images.
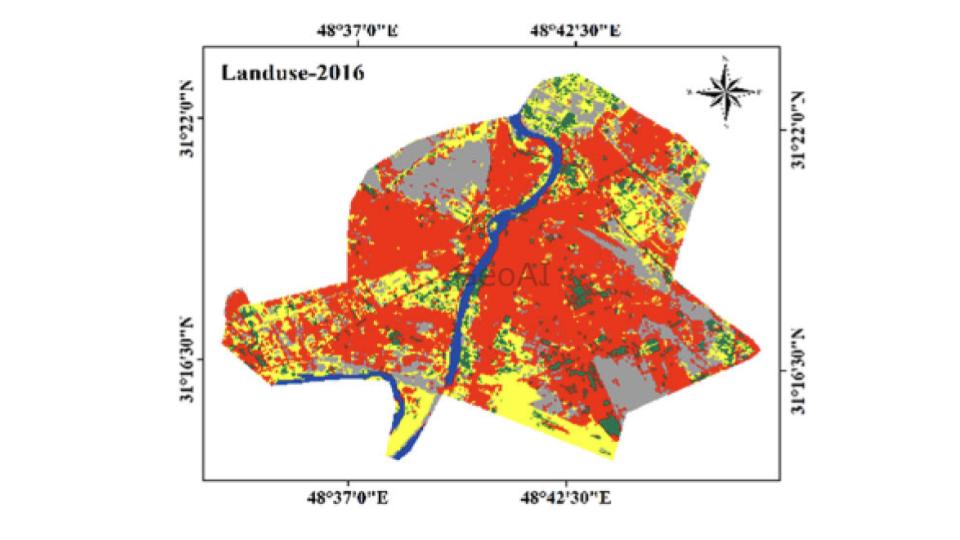
In recent years, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and geospatial technology, known as GeoAI, has revolutionized vegetation monitoring and analysis. GeoAI algorithms use satellite imagery, point cloud data, and thermal images to make a vegetation mapping and tree crown visualization. GeoAI integrate Land Surface Temperature and Land Mapping data to analyse the impact of vegetation to UHI effect.
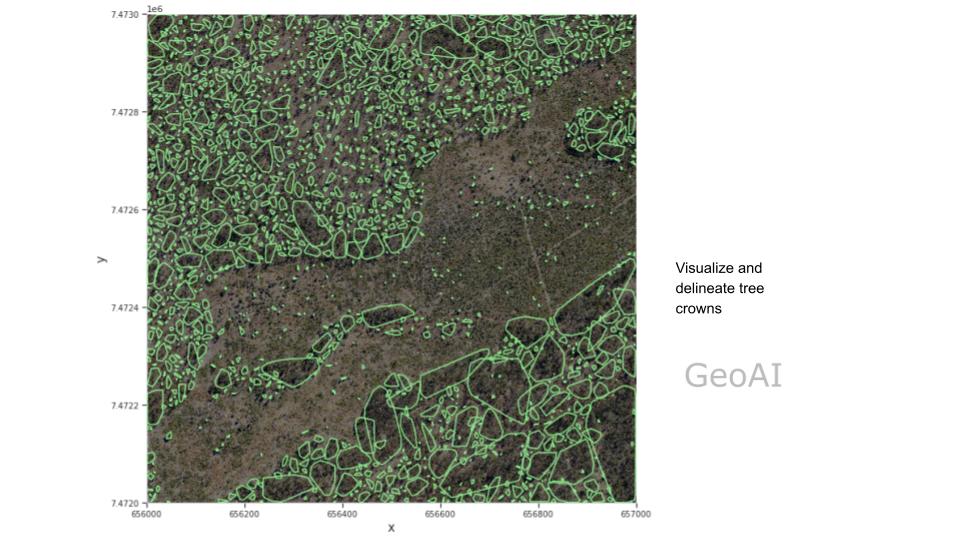

Digital Twin for Vegetation Analysis
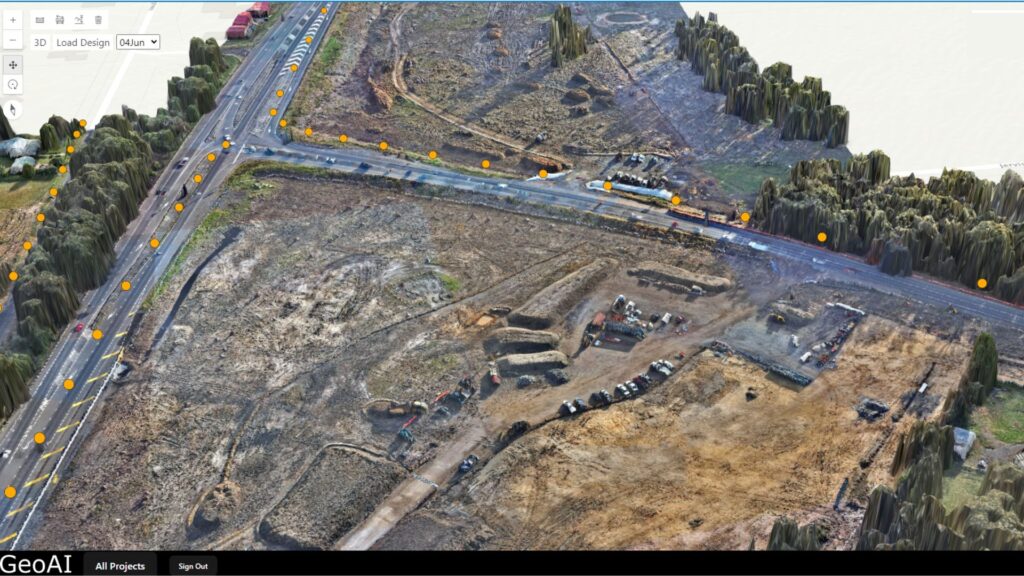
The potential of Digital Twin technology for vegetation analysis is greatly enhanced by the use of UAV LiDAR systems. By creating a highly detailed, dynamic 3D representation of natural environments, a Digital Twin allows for precise monitoring of vegetation health, growth patterns, and biomass over time. UAV LiDAR captures intricate data from difficult-to-reach areas, providing insights into canopy structure, plant density, and even individual tree metrics. This real-time digital model enables land managers, ecologists, and urban planners to simulate environmental changes, assess the impact of deforestation or urbanization, and optimize land-use strategies for sustainability.

360 Panoramic Viewer for Vegetation Analysis
Mounting a 360-degree camera on a car offers significant potential for vegetation analysis by providing a comprehensive, real-time view of plant life and landscapes during ground-level surveys. This approach allows for the capture of high-resolution imagery from multiple angles, covering wide areas efficiently as the vehicle moves through diverse terrains. The captured images can be processed using AI and computer vision techniques to analyze vegetation health, monitor growth patterns, detect species diversity, and identify areas affected by disease or environmental stress. Unlike aerial methods, a car-mounted 360 camera captures vegetation details at lower altitudes, making it ideal for assessing under-canopy plant life, roadside vegetation, and urban green spaces.
Category List
- 3D Point Cloud
- Artificial Intelligence
- Asset Management
- Digital Twin
- Featured
- Hardware
- Knowledge Graph
- LiDAR
- News
- Site Monitoring
- Vegetation Monitoring
- Virtual Reality
Recent Post
- Asset Inventory Mapping with GeoAI: Complete Road Asset Capture Using Laser Scanning and Profiling
- Mobile Laser Scanner and Laser Profiler: Dual Approach to Road Surface Condition Surveys
- Edge Pavement Detection: Using LiDAR and AI for Road Asset Management
- What is Digital Surface Model (DSM)?
- Happy New Year 2026 from GeoAI