What is Digital Terrain Model (DTM)?
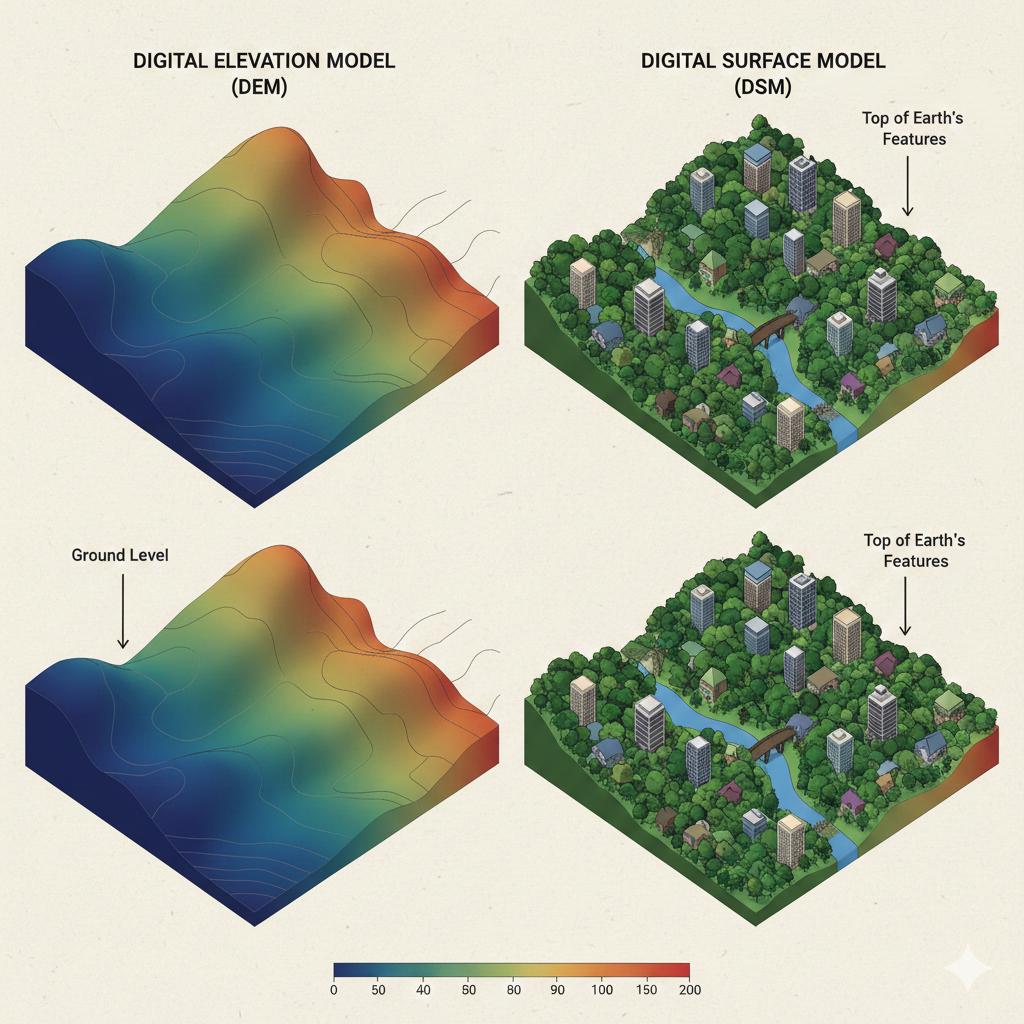
A digital terrain model (DTM) is a detailed three-dimensional representation of the ground surface, accurately reflecting the earth’s bare topography. Unlike digital surface models (DSM) that capture everything visible from above including trees, buildings, vehicles, and other structures, a DTM is specifically designed to show only the underlying terrain. This “bare earth” model is foundational for a wide range of applications in engineering, environmental science, urban planning, and infrastructure development.
How Does a Digital Terrain Model Work?
A digital terrain model consists of elevation data points that describe the height of the ground at specific locations. We can arrange these points as a regularly spaced grid, a triangulated irregular network (TIN), or as contour lines. The main purpose of a DTM is to give an accurate, high-resolution map of the true earth surface. It allows users to analyze natural and artificial landforms without the interference of above-ground objects.
| Model Type | What It Represents | Common Uses |
| Digital Surface Model (DSM) | All surfaces (ground + objects) | Urban planning, line-of-sight, solar studies |
| Digital Terrain Model (DTM) | Bare earth/ground surface only | Engineering, flood modeling, earthworks |
| Digital Elevation Model (DEM) | Generic term (can be DSM or DTM) | Mapping, GIS, general terrain analysis |
Creation Methods for Digital Terrain Models
The most common techniques for creating a digital terrain model include:
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
A laser scanner, mounted on a vehicle, aircraft, or drone, emits thousands to millions of laser pulses per second. These pulses reflect off surfaces and return to the sensor, measuring distances and generating a dense cloud of 3D points. Then, we use advanced algorithms to classify and filter these points, separating the ground from non-ground features such as trees and buildings.
Photogrammetry
Using overlapping aerial photographs or drone images, specialized software extracts elevation information by identifying common features in multiple images. While photogrammetry is highly effective in open areas, extra processing is often needed to remove above-ground features and generate a true DTM. Advanced AI algorithm usually used to classify and separate the ground and non-ground features.
Traditional Surveying
For small or highly detailed projects, ground-based methods such as total stations or GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) can be used to collect accurate elevation data point by point.
How to get the ground surface?
After collecting point cloud or image data, the next step is filtering out all non-ground points. This can be a complex process in areas with dense vegetation or urban environments. Advanced classification algorithms enhanced with AI are used to distinguish between ground and non-ground returns. The result is a highly accurate representation of the terrain. This data then ready for further analysis and modeling.
Applications of Digital Terrain Models
Digital terrain models are a fundamental resource in many industries. Some of the most common uses include:
- Flood Risk Assessment: By analyzing the flow of water across the ground surface, DTMs help predict areas at risk of flooding and guide the design of drainage and flood mitigation systems.
- Road, Railway, and Infrastructure Design: Engineers use DTMs to plan alignments, calculate earthworks, and ensure proper grading for new construction projects.
- Slope Stability and Landslide Analysis: DTMs allow for precise measurement of slopes and identification of areas susceptible to landslides or erosion.
- Mining and Earthworks: Accurate terrain models are essential for calculating cut and fill volumes, monitoring progress, and planning site development.
- Environmental Management: DTMs support habitat mapping, forest management, watershed analysis, and environmental monitoring.
- Urban Planning and Digital Twins: Modern cities use DTMs as a base layer for smart city modeling, asset management, and the integration of real-world conditions into digital twins.
The Advantages of Using a Digital Terrain Model
The benefits of a digital terrain model go beyond simple elevation mapping:
- Precision: DTMs deliver detailed, centimeter-level accuracy, making them ideal for design, analysis, and as-built verification.
- Efficiency: Automated processing of laser scan data enables large-scale terrain modeling over kilometers of landscape in a fraction of the time required by traditional surveys.
- Versatility: DTMs are compatible with CAD, GIS, and BIM platforms, providing seamless integration for engineers, planners, and designers.
- Decision Support: By revealing the true shape of the ground, DTMs empower better, data-driven decisions in every stage of a project.
GeoAI’s Digital Terrain Model Services
At GeoAI, we combine advanced LiDAR scanning technology with intelligent data processing to deliver reliable digital terrain models tailored to your project’s requirements. Our systems can efficiently capture high-resolution data across urban, rural, or forested areas. Our in-house algorithms ensure precise ground extraction, even in challenging environments. As a result, we can generate DTMs ready for engineering, environmental, or GIS applications.
Whether you need ground models for road design, site planning, or digital twin integration, our team can provide DTM outputs in formats such as raster grids, TINs, contour lines, or vector files suitable for your software ecosystem.
Get Started with Digital Terrain Models
Interested in learning more about how a digital terrain model can benefit your next project? Contact GeoAI for a consultation or to request a sample dataset. Our experts are ready to support your needs in surveying, construction, infrastructure, and digital twin development.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
A digital terrain model (DTM) represents the bare ground surface, with all vegetation, buildings, and other above-ground features removed. In contrast, a digital surface model (DSM) includes everything on the earth’s surface, such as trees, houses, and power lines.
The accuracy of a DTM depends on the data collection method and the environment. LiDAR-based DTMs typically achieve vertical accuracy of 5–15 cm, but accuracy can be higher in open areas and slightly lower in dense vegetation or urban locations.
DTMs are widely used for engineering design, flood modeling, road and railway planning, slope analysis, earthworks calculations, environmental monitoring, and as a foundation for GIS and digital twin platforms.
Yes, you can use drone photogrammetry to generate digital terrain models, especially in open areas. However, you will need additional processing to remove above-ground features to create a true bare earth model.
At GeoAI, we can provide DTMs in multiple formats, including raster grids (e.g., GeoTIFF), point clouds (LAS/LAZ), contour lines (SHP, DXF), and TINs, depending on your project requirements and software preferences.
We use advanced classification algorithms, sometimes supported by AI, to automatically separate ground points from non-ground points in the raw data. Our quality control processes ensure that the final DTM is an accurate reflection of the bare terrain.
GeoAI combines the latest LiDAR technology with smart data processing workflows, ensuring accurate, reliable, and timely digital terrain models. We have experience with complex sites, from urban areas to forests, and can deliver outputs tailored to engineering, construction, or GIS applications.
Category List
- 3D Point Cloud
- Artificial Intelligence
- Asset Management
- Digital Twin
- Featured
- Hardware
- Knowledge Graph
- LiDAR
- News
- Site Monitoring
- Vegetation Monitoring
- Virtual Reality
Recent Post
- Pavement Defect Detection with GeoAI: Harnessing Laser Scanners and Profilers
- Asset Inventory Mapping with GeoAI: Complete Road Asset Capture Using Laser Scanning and Profiling
- Mobile Laser Scanner and Laser Profiler: Dual Approach to Road Surface Condition Surveys
- Edge Pavement Detection: Using LiDAR and AI for Road Asset Management
- What is Digital Surface Model (DSM)?