Vegetation Map Australia
Vegetation mapping plays a critical role in understanding Australia’s unique ecosystems, supporting environmental management, and facilitating sustainable development. This article explores the existing vegetation maps in Australia, their benefits, the process of creating them. Additionally, the role of cutting-edge technologies like remote sensing and GeoAI in revolutionizing vegetation mapping.
Existing Vegetation Maps in Australia
Australia boasts several well-known vegetation maps that serve as invaluable tools for ecological and planning purposes. These include:
- NVIS (National Vegetation Information System): Provides comprehensive data on the extent and distribution of vegetation types across Australia.
- Queensland Regional Ecosystem Mapping: Detailed maps highlighting vegetation communities specific to Queensland.
- Native Vegetation Regulatory Map (NSW): The native vegetation regulatory map of New South Wales is a tool landholders can use when considering how best to manage native vegetation on their land.
- Victoria Vegetation Map: Vicmap Vegetation contains topologically structured digital datasets depicting trees or areas of woody cover across the state of Victoria. This resource can assist users in environmental analysis, risk management, and map production activities. Notably, its customers include utilities, resource managers, local governments, cartographers, and emergency services organizations.
- Western Australia Vegetation Data: Similarly, the vegetation dataset for Western Australia supports various decision-making purposes, offering valuable insights for environmental and planning needs.
- State and Territory Vegetation Mapping Initiatives: In addition, each state and territory maintains localized vegetation maps, ensuring region-specific data is available for targeted applications.
Vegetation Map Australia are crucial for conservation, land use planning, and climate change mitigation strategies. Therefore, it is important to have a comprehensive data of vegetation map Australia updated.
Benefits of Vegetation Maps
- Environmental Conservation: They help identify critical habitats, monitor biodiversity, and plan conservation efforts.
- Land Use Planning: Essential for sustainable urban planning and agricultural development.
- Disaster Management: Aid in assessing fire risks and planning disaster response strategies.
- Carbon Sequestration: Support climate change mitigation by tracking vegetation’s role in carbon storage.
- Research and Education: Provide data for ecological studies and promote awareness of Australia’s diverse vegetation.
How to Make a Vegetation Map
Creating a vegetation map involves the following steps:
- Data Collection: Gather information through field surveys, remote sensing technologies such as satellite, high resolution camera, laser scan, or existing datasets.
- Classification: Categorize vegetation types based on species, density, and other ecological factors. The classification procedure can be conducted using manual classification or automatic classification using Geospatial Artificial Intelligence (GeoAI).
- Geospatial Analysis: Use GIS (Geographic Information Systems) to map and analyze the spatial distribution of vegetation.
- Validation: Cross-check results with field data to ensure accuracy.
- Visualization: Present data through user-friendly and interactive maps such as Cesium Ion, Open Street map,
Role of Remote Sensing in Vegetation Mapping
Advanced technologies have transformed vegetation mapping by making the process more efficient and accurate.
- Satellite Imagery: Provides large-scale vegetation data, offering insights into growth trends, density, and seasonal changes. Popular sources include Sentinel-2 and Landsat.
- Drone Surveys: Offer high-resolution imagery for detailed, localized vegetation analysis.
- LiDAR (Laser Scanning): Measures vegetation structure and canopy height with unmatched precision, aiding in 3D vegetation modeling.
- Multispectral and Hyperspectral Sensors: Detect specific wavelengths to identify plant health, species, and stress levels.
How GeoAI Can Help You Make a Vegetation Map
High-resolution satellite imagery and LiDAR point cloud data offer significant potential to shift forest monitoring from traditional field surveys to AI-driven remote sensing solutions. Although conventional methods exist, they often rely on labor-intensive feature engineering and lack the capability to simultaneously utilize both spatial and spectral data effectively.
GeoAI integrates artificial intelligence with geospatial data, offering powerful tools for vegetation mapping. Here’s how GeoAI can assist:
- Data Integration: Firstly, combine satellite, drone, and LiDAR data into a unified, coherent map. By combining different data, we can have more comprehensive information to be analysed. Eventually, a complete vegetation map can be generated to help you improve your decision making.
- Automated Analysis: Secondly, leverage AI-driven models to efficiently classify vegetation types, evaluate plant health, and monitor changes over time.
- Predictive Modeling: Furthermore, utilize climate data and historical trends to predict future vegetation changes, enabling proactive and informed decision-making.
- Customization: Finally, create customized maps tailored to address specific project requirements, whether for agricultural planning, conservation initiatives, or other specialized applications.
Leveraging AI in Vegetation Mapping with GeoAI
GeoAI uses advanced AI technologies to enhance vegetation mapping.
- LiDAR point cloud data will be used to detect and segment vegetation. Meanwhile, TIFF spectral data will be utilized to produce a vegetation index. Consequently, this combination will generate a tile that integrates both spectral and spatial information.
- Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning process for automatically calculate vegetation health such as NDVI, land cover, grass cover, canopy height, and biodiversity classification.
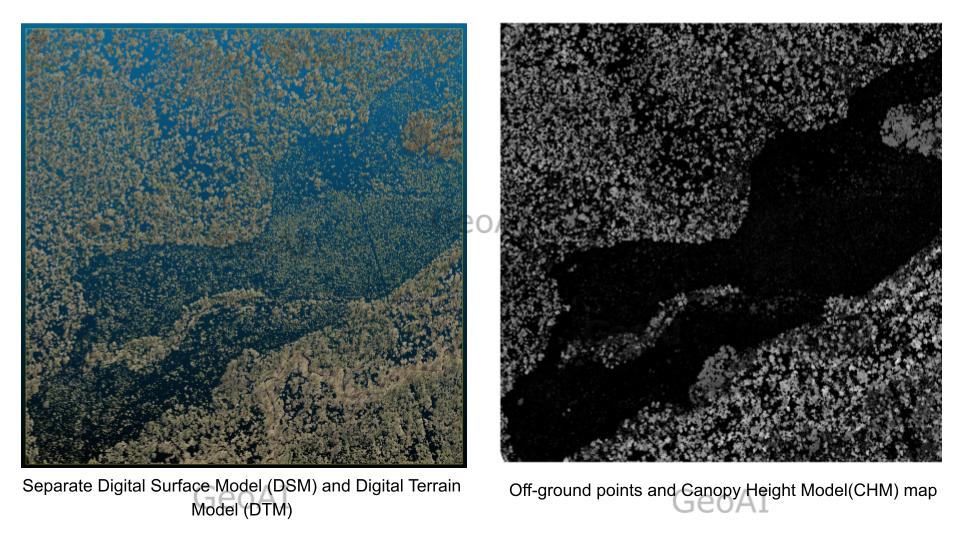 Canopy Height Mapping
Canopy Height Mapping - Canopy height mapping. Mark each tree top by local maxima. The coordinates of tree tops are calculated to match with field notes in later steps.
 Tree top marking by using local maxima of the point cloud
Tree top marking by using local maxima of the point cloud - Visualise and delineate tree crowns. Crowns are defined using density-based spatial clustering. As a result, we can see each tree crowns automatically.
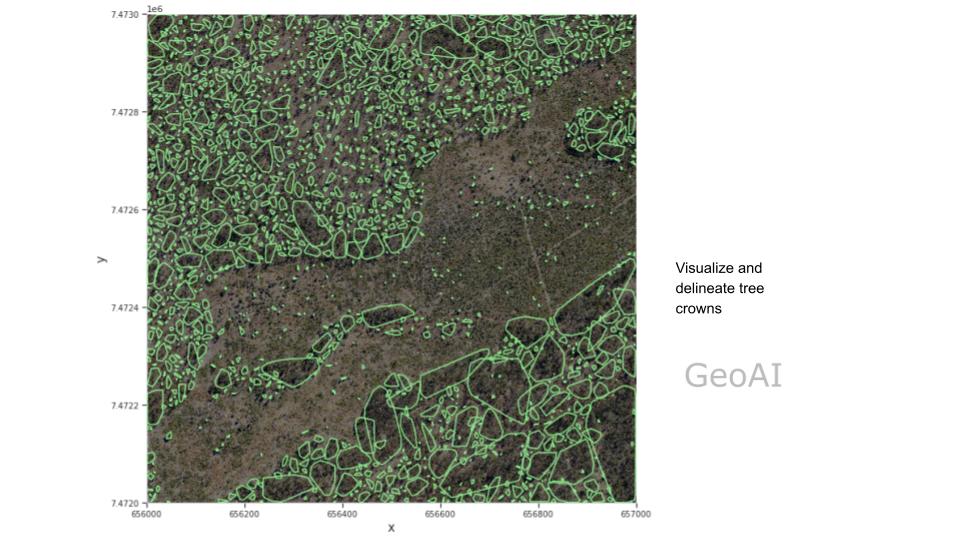 Visualize and delineate tree crowns
Visualize and delineate tree crowns - Automatic Tree/shrub calculation. For each crown, we save a row of polygon with its tree/shrub top coordinate. Meanwhile, the area and height of each crown can be calculated.
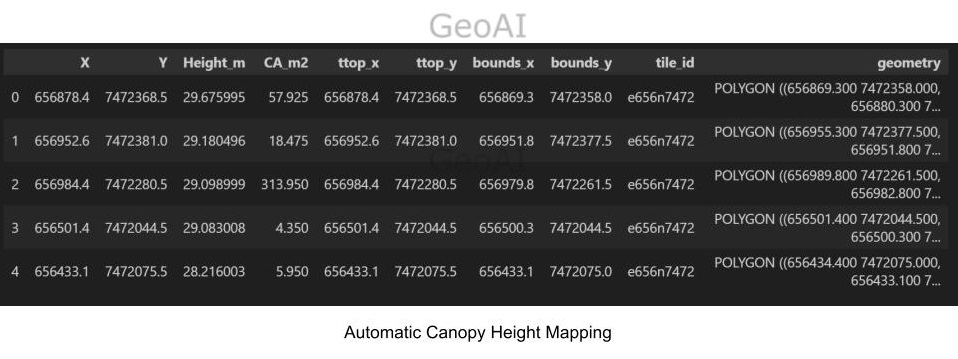 Automatic Canopy Height Mapping
Automatic Canopy Height Mapping - Classification of plant coverage based on NDVI data.
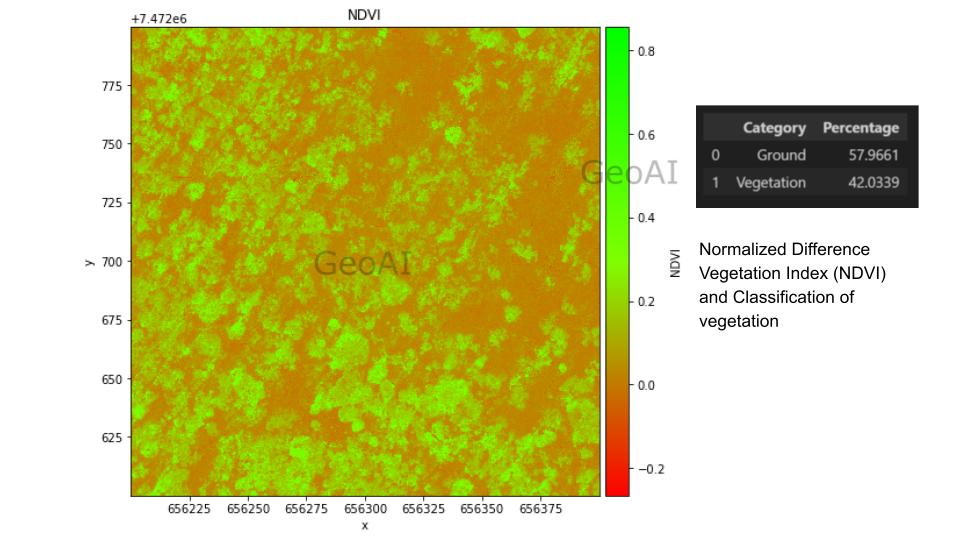 Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Classification of vegetation
Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Classification of vegetation - Automatic Classification. Combine both NDVI and CHM data, we can achieve more detailed stratification. For example, when tall shrubs can grow as high as 8 meters, it’s hard to separate it from short trees purely by height. Based on the principle that trees in general have higher NDVI value, we can classify ground, trees, and shrubs automatically. There is a good consistency with precious result that made this method is accurate.
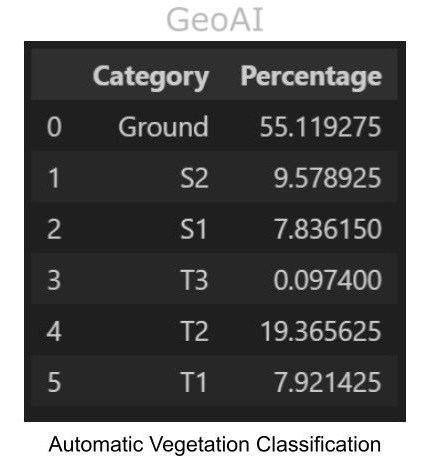 Automatic Vegetation Classification
Automatic Vegetation Classification - Natural Language Processing: Analyze textual data, such as reports and historical records, to gain enriched mapping insights. Moreover, this information is essential for complementing current spatial data obtained from laser scanning and satellite imagery.
- Real-Time Data Processing: Additionally, incorporate live data streams from IoT devices and satellites to produce up-to-date maps.
GeoAI’s expertise in geospatial analysis and AI technologies ensures precise and reliable vegetation maps tailored to your needs. Whether for conservation, agriculture, or urban planning, GeoAI can empower you to get the full potential of vegetation mapping.
To learn more about how GeoAI can support your vegetation mapping projects, Contact Us Today!
Category List
- 3D Point Cloud
- Artificial Intelligence
- Asset Management
- Digital Twin
- Featured
- Hardware
- Knowledge Graph
- LiDAR
- News
- Site Monitoring
- Vegetation Monitoring
- Virtual Reality
Recent Post
- Pavement Defect Detection with GeoAI: Harnessing Laser Scanners and Profilers
- Asset Inventory Mapping with GeoAI: Complete Road Asset Capture Using Laser Scanning and Profiling
- Mobile Laser Scanner and Laser Profiler: Dual Approach to Road Surface Condition Surveys
- Edge Pavement Detection: Using LiDAR and AI for Road Asset Management
- What is Digital Surface Model (DSM)?